
Indonesia’s Journey to Better Health and Wellness – Part 2
This is part two of our series on Indonesia’s healthcare. We’re exploring future technological breakthroughs in healthcare. Indonesia is just starting to use tech in healthcare. Early efforts, such as Telemedicine and Online Booking, have already made healthcare more efficient and convenient. Upcoming advancements, especially in genomics, could bring over $100 billion in economic gains. With the government’s backing, we anticipate swift advancements in the near future.
Hit us if you wish to learn more on the Indonesia healthcare sector. Our earlier newsletters forming part of this series can be accessed here.
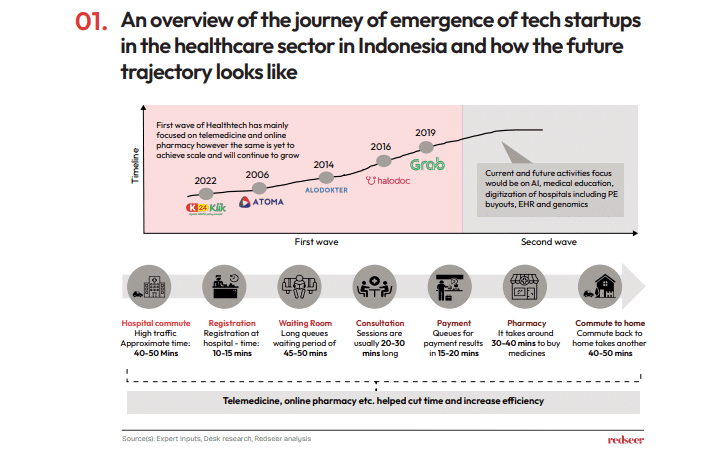
The first wave of sectors focused on making healthcare faster and more efficient. The next wave targets improving healthcare quality with cutting-edge technology. Initially led by eHealth solutions such as telemedicine, appointment booking, and online medicine delivery, the future will see a rise in hospital digitization, preventive care, genomics, and similar fields, all enhanced by AI innovations.
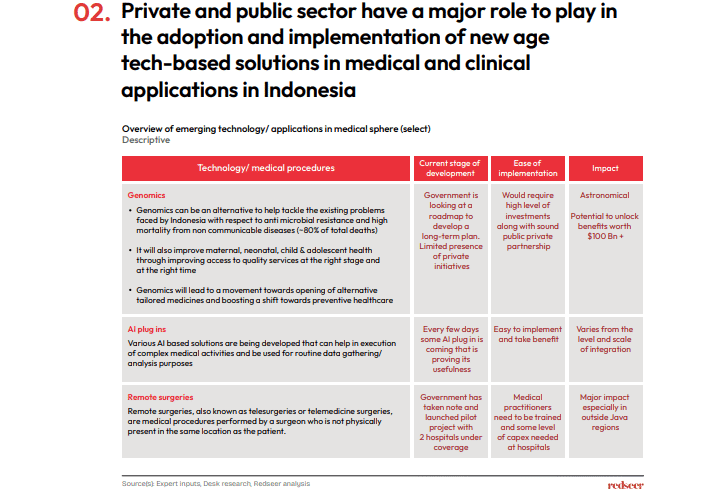
Telemedicine and other eHealth services, already in place, are poised for further evolution. New technological breakthroughs are expected to greatly improve Indonesian healthcare. The government, acknowledging this potential, is launching programs and pilot studies to support these emerging medical technologies.
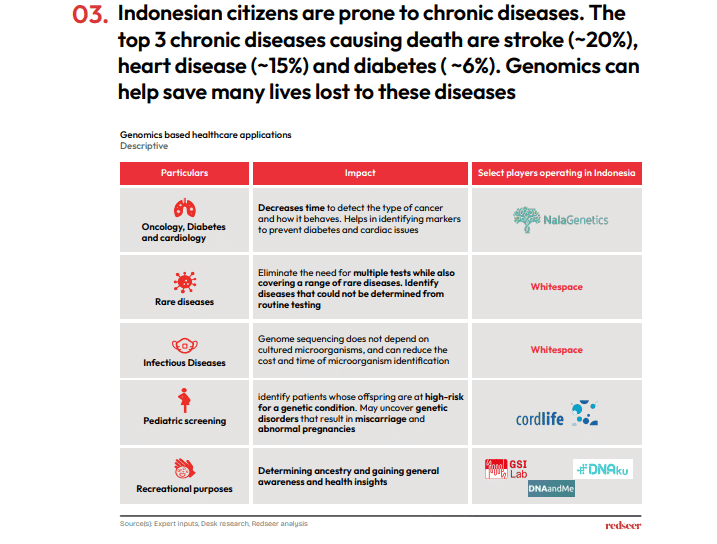
Genome sequencing allows doctors to quickly identify cancer and recommend treatments more effective than chemotherapy. It improves pediatric and prenatal screening, detecting rare and genetic conditions such as Down syndrome early on. Importantly, genomics is vital in fighting infectious diseases like Tuberculosis, a major concern in Indonesia. The healthcare cost savings for Indonesia could surpass $100 billion.
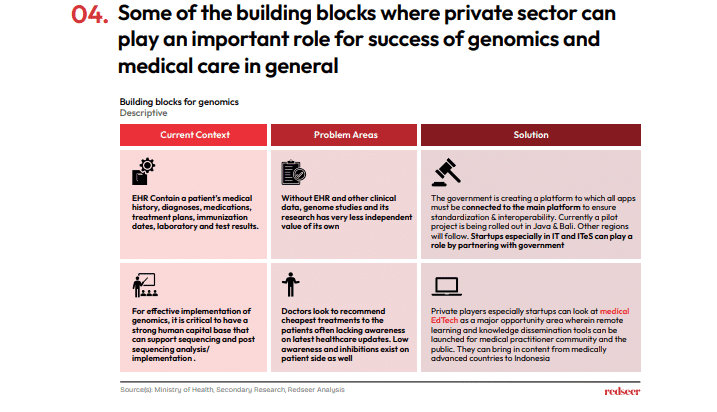
Genomics and its associated fields need a supportive, mature ecosystem to flourish. Key to this success are a skilled medical workforce and a robust electronic health records (EHR) system. Here, tech-savvy new players can make substantial contributions, aiding both the government and public health institutions. The creation of EHRs is vital for utilizing genomic data in developing practical applications and clinical solutions. Additionally, the private sector’s involvement in establishing data centres and new bio banks is essential for support.
Want to get strategic guidance?
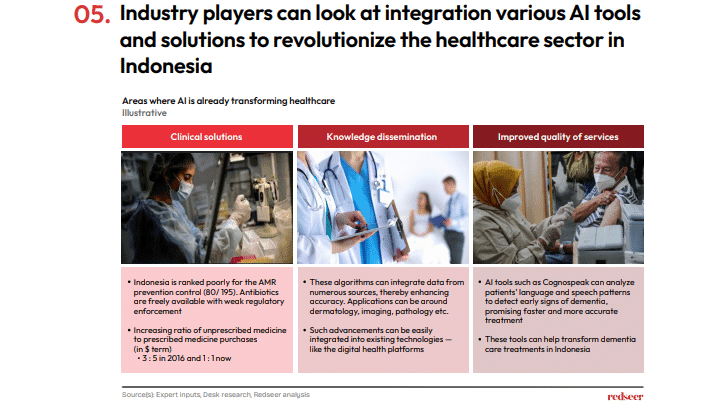
• AI tools have pinpointed novel antibacterial microbes that tackle multi-drug resistant bacteria, showing significant promise in clinical fields.
• Platforms such as Chat GPT have excelled in passing advanced medical exams.
• Moreover, incorporating AI into medical service delivery could result in the early diagnosis of diseases.

Written by
Roshan Behera
Partner
Roshan is a Partner based in Singapore and focuses on Southeast Asia. His sector coverage includes e-commerce, logistics, fintech, eB2B, on-demand services, and other emerging sectors.
Talk to me
Value Retail: The Quiet Force Reshaping MENA’s Consumer Economy

India’s Defence DeepTech Flywheel: The $6Bn Market Nobody’s Watching

Ready-to-Eat Brands Are Leaving 85% of Addressable Consumers on the Table
