1. The omnichannel adoption journey includes both experiential technologies along with basic features and restructured business models
Published on: Nov 2019
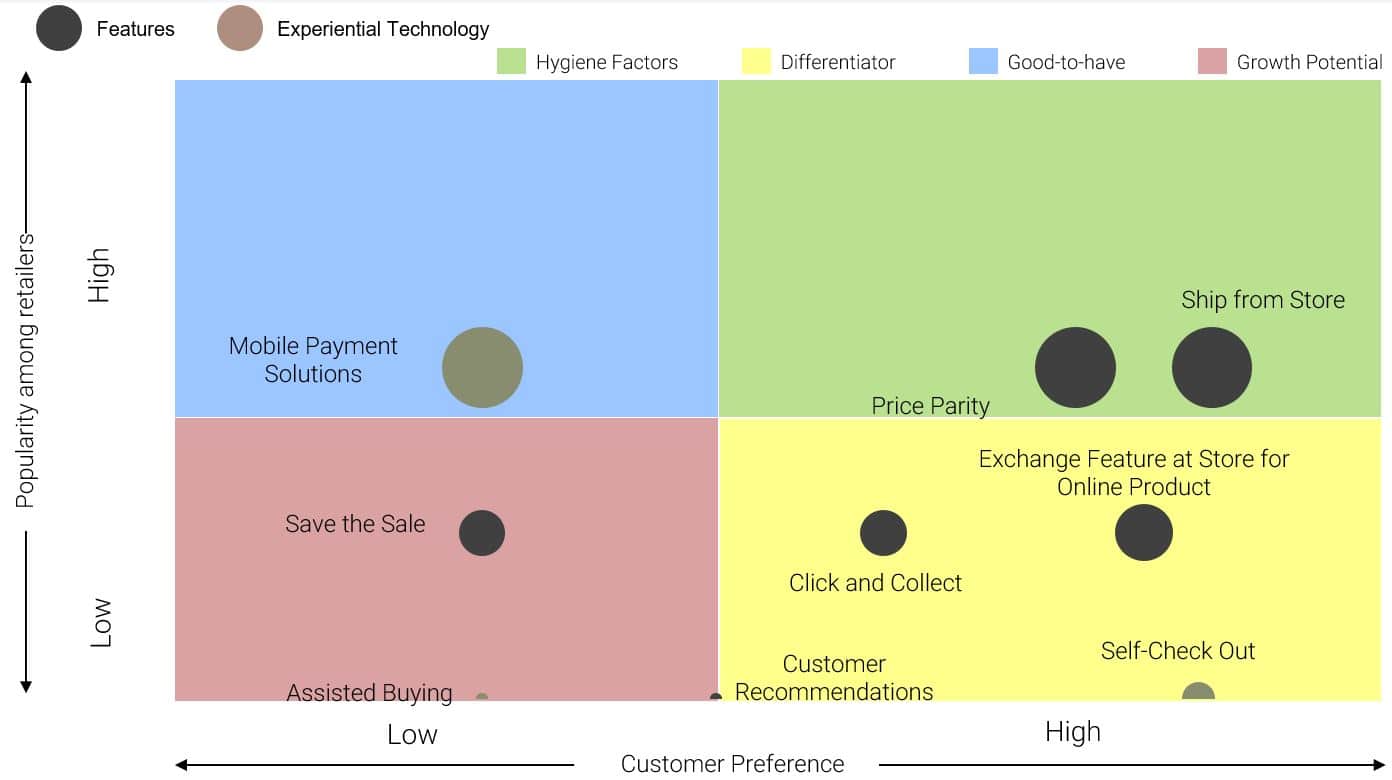
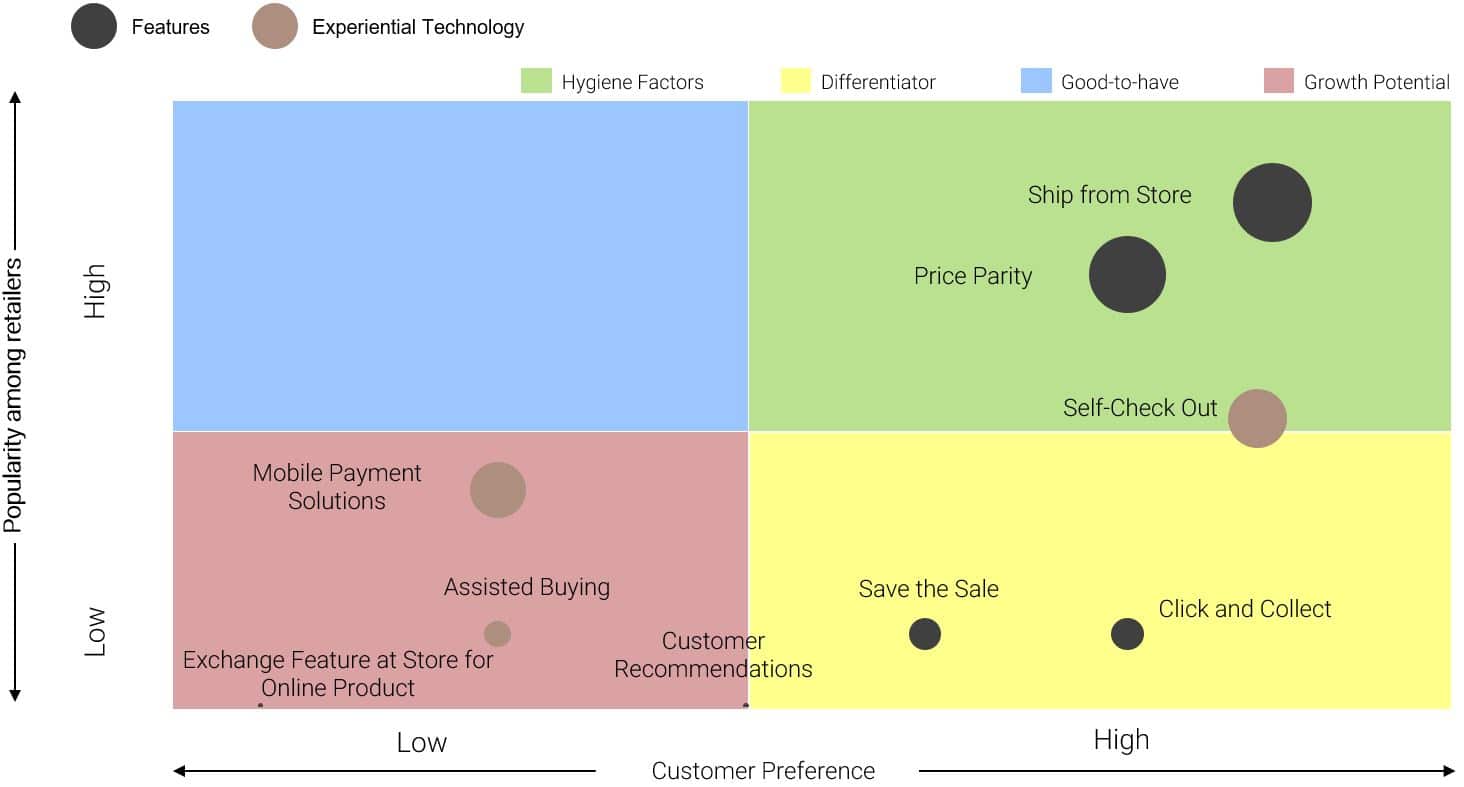
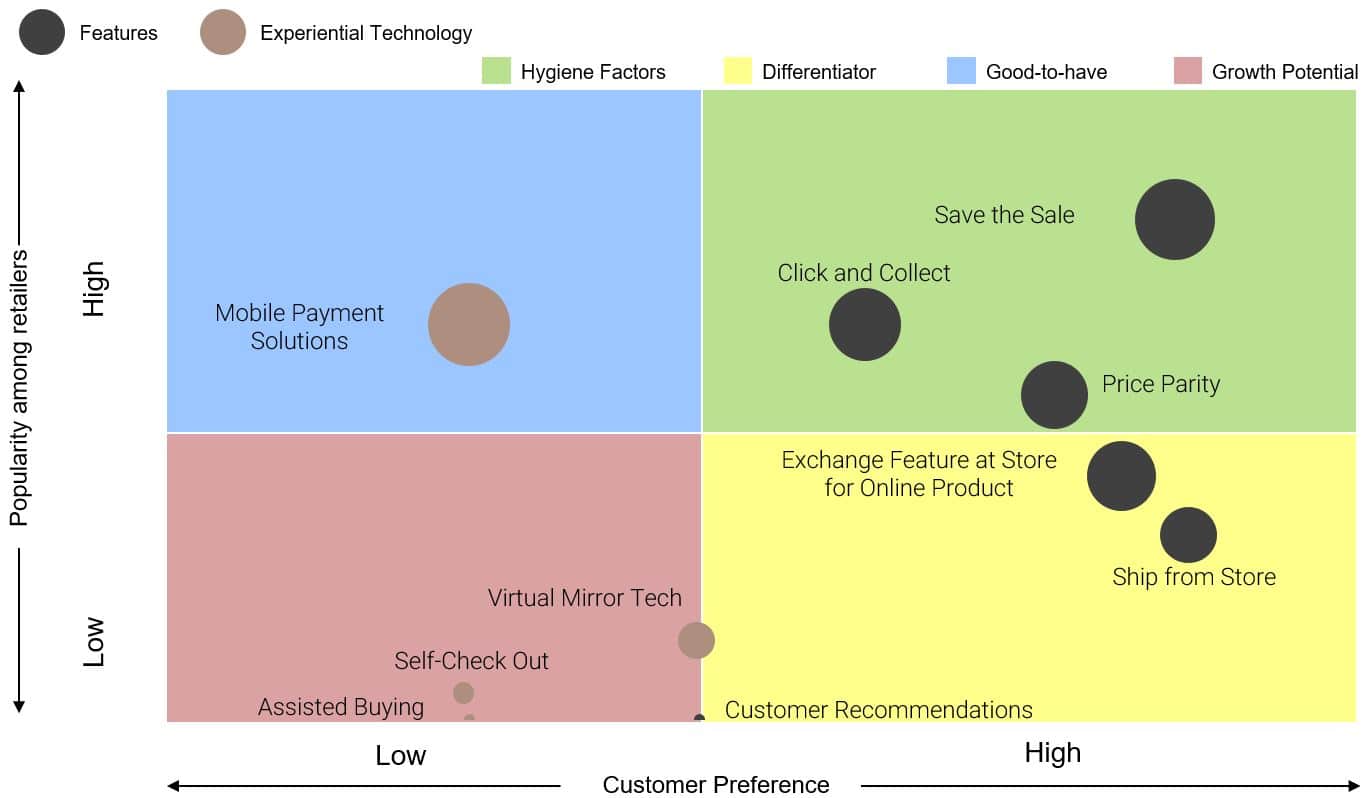
Omnichannel adoption is facilitated by the implementation of certain features, technology and restructuring in one’s business model that enables the integrated approach across channels.
Across businesses, inventory integration becomes a major need for omnichannel adoption, with modules like Order Management System, Warehouse Management System and the Enterprise Resource Planning System working together to ensure that there is a single view of the inventory from the store and warehouse. This builds in greater transparency and increased efficiency in replenishment, fill rates and fulfilment time to the customers.
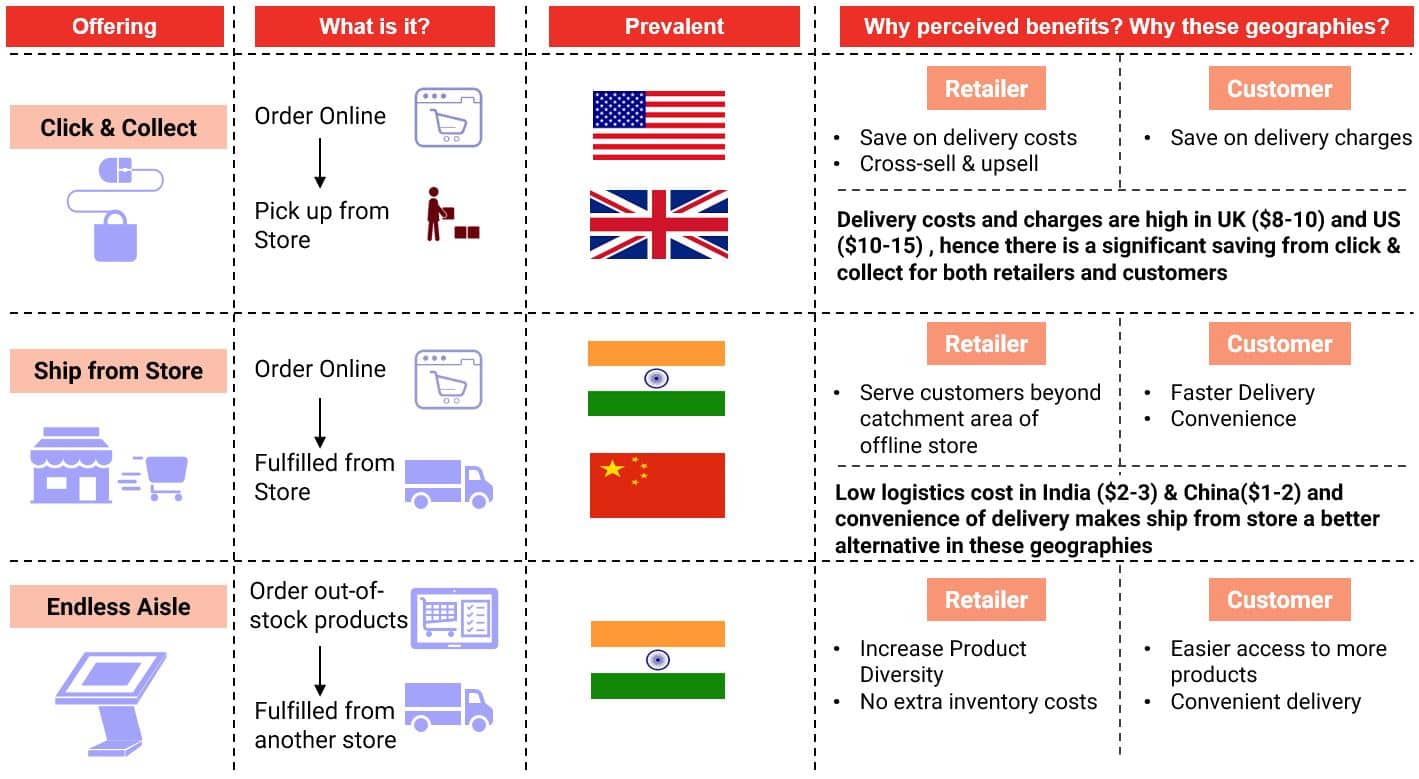
The ability to “Self-Check Out” at retail B&M outlets is another feature that characterises omnichannel giving the customer the ability to skip long queues and avail automatic check out kiosks. Customer deliveries have also given rise to two more models widely prevalent across the world including “Click and Collect” and “Ship from Store”. “Click and Collect”, particularly popular in the UK provides customers with the chance to order products online and collect them from the store, giving retailers a chance to cross-sell and up-sell their products as the store experience helps in inducing impulse purchases. In economies like India, with lower logistics costs, models like “Ship from Store” see wider traction. In this model, home deliveries are initiated from local stores acting as fulfilment centres as opposed to warehouses.
Customer retention is also ensured through features like “Save the Sale” or “Endless Aisle”, which ensures that consumers can access out of stock products within the store from online platforms. Some retailers also provide customers with the opportunity to exchange products at the store post purchasing online, keeping the customers satisfied with their purchase experience.
From an experience level, features like virtual mirrors, empower customers to get a look and feel of the product even without trying it on, while assisted buying, facilitated by store personnel with devices that enable viewing previous purchase history, add largely to the in-store shopping experience of the customers.
Across countries, the maturity of omni-channel elements is largely dependent on the development index, labour and logistics costs. This triggers higher adoption of click and collect in developed economies and “Ship from store” in India.
2. Despite the high online traction, omnichannel adoption for electronics has been low in India
Electronics as a category has 47% of its sales from organized channels emerging from online, with mobile phones, comprising 67% of the online channel to organized market ratio. Studying the market as a whole, one finds that price parity is a major hygiene factor with differential pricing across channels being a major factor that needs to be sorted to embrace omnichannel for this category. However, in India, omnichannel adoption for electronics retailers has been quite low, with a smaller number of pan-India retail chains for electronics, and brands not being particularly active on their direct to customer online channels.
3. Grocery and General Merchandise categories have adopted price parity and mobile payments for consistent experience and convenience
Grocery and General Merchandizing has limited traction on online channels in general, and even in that space, e-retailers have been more successful in creating a niche. The omnichannel adoption across brands has been generally low with few big players adopting click and collect model, and direct delivery through their online channel. Price parity has been adopted largely across retailers to prevent skewed growth in one channel. Some other features that are highly essential and akin to category growth drivers are,” Self-checkout” to reduce the high wait time associated with shopping in B&M stores and delivery models like “Ship from store”, to ensure greater convenience and fresh goods.
4. Fashion has witnessed the highest adoption among categories and fashion brands and retailers have seen a substantial impact on their business with omnichannel
Among all categories, both fashion brands and retailers have been proactive in adopting omnichannel as a part of their strategy and have incorporated both hygiene factors as well as differentiators in their operations. “Ship from store” and “Exchange of online purchase at the offline store” has been particularly high in its adoption given that it falls under high preference factors for customers. Numerous retailers have also opted for the “Click and Collect” model in fashion.
In the category, discounts and deals have been pushing the omnichannel play. It is expected that a wider assortment of products will drive growth in the near future. However, strikingly, endless aisle, which is a solution to major problems of all retailers, has seen low traction.