The Indian MSME growth story is being catalyzed by two ongoing watershed movements– the first being the transition of the nation into a paperless economy and the second being the increased formalization of the informal economy. At the juncture of these two movements, the sector has played a critical role in the expansion of the formal economy from 48% in 2017 to 60% in 2023.
MSMEs in India contribute to 30% of the nation’s GDP across multiple divisions including apparel, footwear, automobiles, handicrafts, agriculture, pharmaceuticals and electronics. As a recognition of their potential, government policies such as ‘China + 1’ provide incentives to enhance their manufacturing capabilities and gain access to critical online tools that open them up to new markets, geographies and demographic groups while engaging with customers in multiple meaningful ways.
The next logical step to channelizing the fullest potential of the vibrant MSME sector is to further eCommerce adoption and seamlessly integrate the utilization of digital payments into business operations at large scale. Currently, 1.5-2.5 million MSME sellers are online with 60% of them making use of digital payments facilities like Net Banking and UPI for their transactions. By the year 2027, internet penetration is expected to reach 80% and e-payment penetration is set to touch 70% overall. The current rate of internet penetration within the MSME sector is at 2-3%, and there is major scope for it to rise to 5-6% by the year 2027. It is also imperative to have as many as 5.5-6 million sellers onboarded on to eCommerce platforms along the same timeline.
With eCommerce adoption MSMEs are set to contribute to 34-40% of the economy
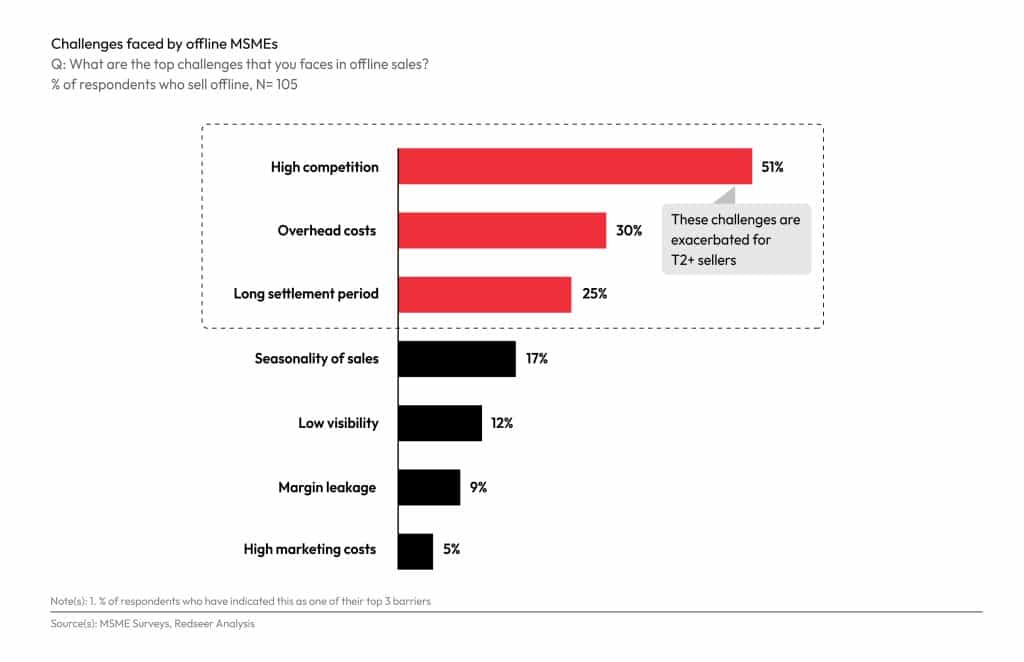
Offline MSMEs face multiple challenges as they compete with established brands that have an online presence. Some of them include decreased visibility, lesser insight into seasonal trends and limited access to marketing tools. One in four MSMEs also report difficulties in recovering dues for extended periods and many of them have indicated that their overhead expenses contribute to their financial burden. Through eCommerce adoption and an online presence, MSMEs can reach out to pan-Indian and international customers who are free to explore products and services at will. In addition to maintaining their competitiveness and enjoying increased visibility at lower marketing costs, eCommerce adoption also facilitates timely payments for MSME participants.
96% of the MSMEs reported a total net profit increase, and 55% of the sellers saw their profits grow by 24% post eCommerce onboarding
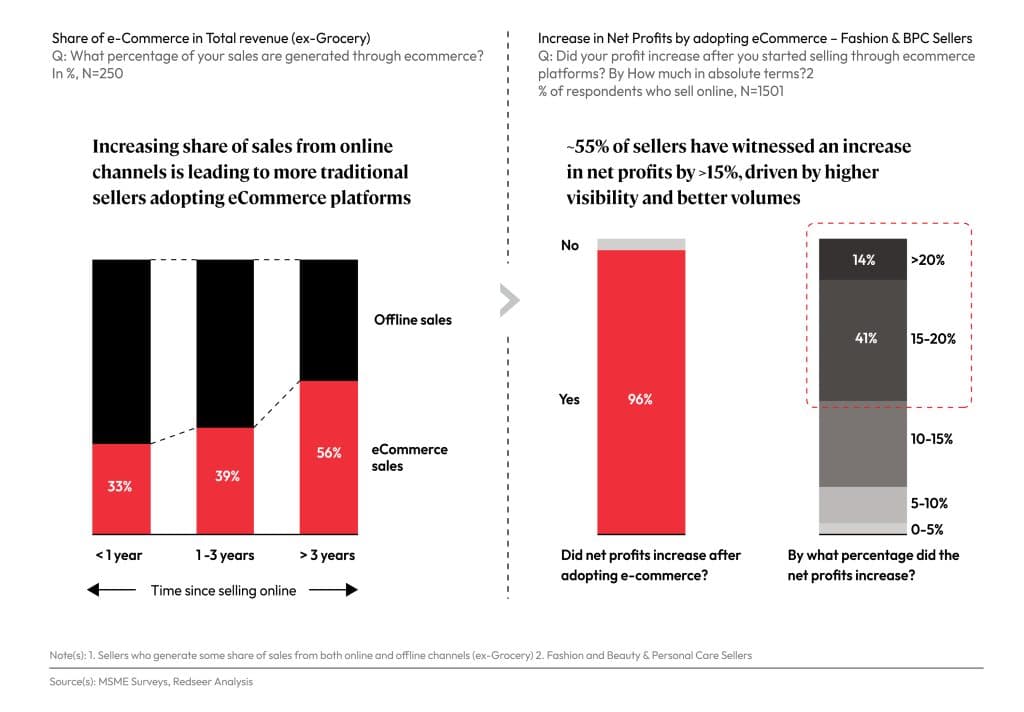
A survey by Redseer reveals that the online revenue for non-grocery sellers accounted for one-third of total sales in the first year of operation. By the third year of the MSME’s eCommerce onboarding, this revenue share is seen to have exceeded 50% of the total sales for the year. Our research has also observed that sellers in categories like Fashion, Beauty, and Personal Care also saw a substantial increase in their net profits. One of the sellers interviewed reported that eCommerce adoption has directly led to the reduction of overhead and sourcing costs and in turn enabled their net profits to grow beyond 50%.
Some of the other benefits of eCommerce adoption include the possibility of business expansion with reduced capital expenditures, increased profitability through the elimination of middlemen and the better financing of working capital courtesy of timely payments. Online channels also enable MSMEs to better understand their customer base and make informed business decisions.
Online MSMEs are to outgrow eTailing at a CAGR of 60-70% and add USD 50 million to the e-Retail market by FY2027
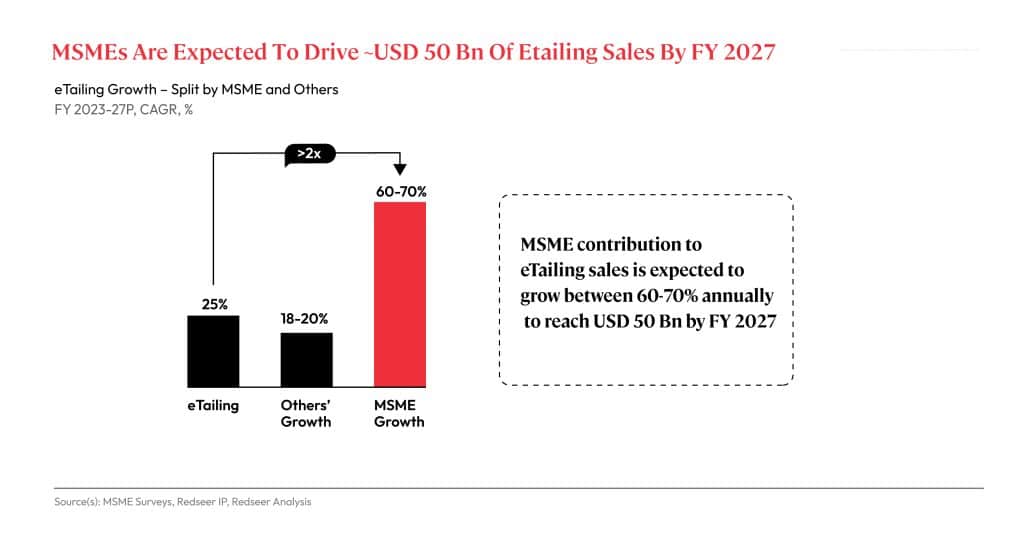
The eTailing sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of 25% through FY2027 and MSMEs will see a 60-70% CAGR growth, substantially outpacing the former. Furthermore, changes to the GST Act and Rules could encourage sellers unregistered under the CGST Act but supplying Goods with a turnover of up to Rs 40 lakhs per annum, and Services with a turnover of up to Rs 20 lakhs per annum to make intra-State supplies. More MSME participation in eCommerce could also signal a major shift in platforms’ vendor policies.
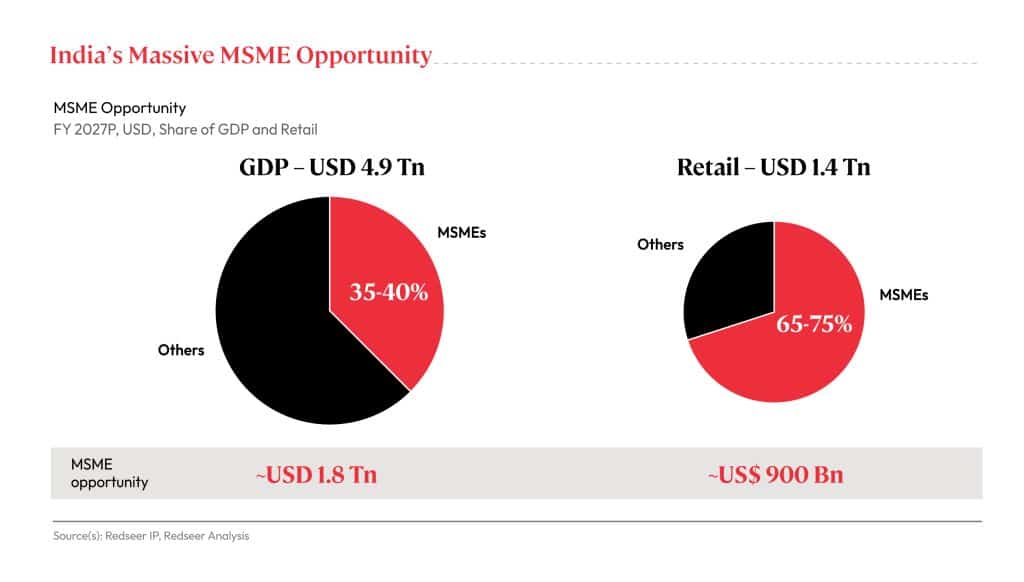
The Indian economy is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8% per year to USD 4.9 trillion in 2027 from USD 3.6 trillion in 2023. Tapping into the potential of the MSME sector will be critical to strengthening India’s position among the fastest growing economies in the world.