The GCC Q-commerce landscape is experiencing a fundamental transformation as platforms evolve beyond their food delivery origins into comprehensive retail ecosystems. While Quick Retail has emerged as a significant growth driver, the competitive dynamics remain highly fluid. This evolution presents both unprecedented opportunities and intense competitive challenges, with market leadership positions shifting frequently as new players disrupt established hierarchies and consumer preferences continue to evolve.
1. Q-commerce market is evolving beyond Food Delivery into Quick Retail
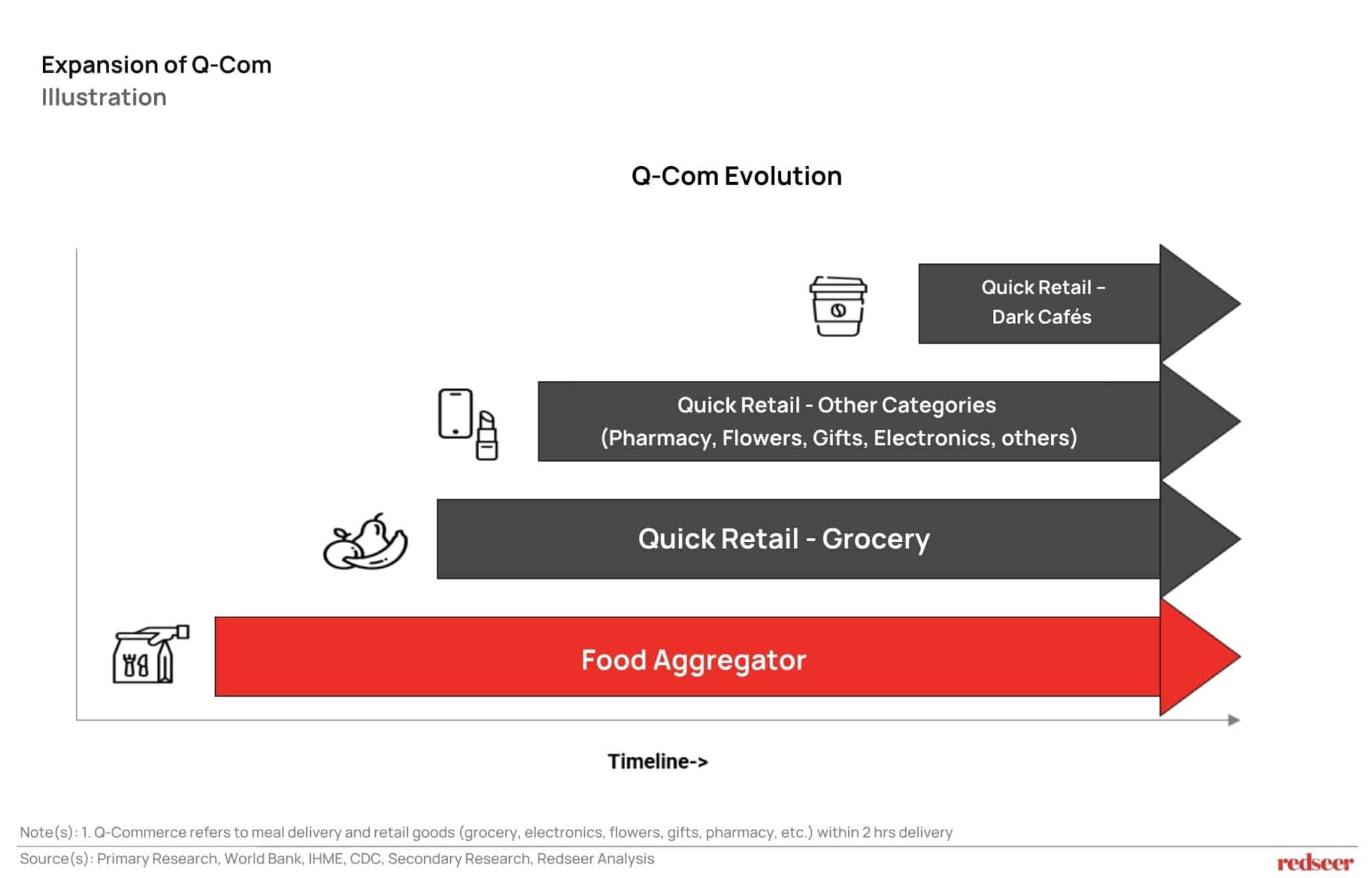
The Q-commerce ecosystem has systematically expanded beyond its food delivery origins into a comprehensive retail platform. What began as meal delivery has evolved through quick groceries and now encompasses diverse categories, including pharmacy, electronics, flowers, and beauty products. The emergence of hybrid models like dark cafés, which blend fast food and grocery offerings, exemplifies this evolution. Platforms are leveraging their existing delivery infrastructure to capture broader consumer needs, transforming from single-category services into multi-vertical retail ecosystems that fulfill diverse consumer demands within minutes.
2. GCC Quick Retail has achieved remarkable growth, increasing from <5% to ~25% of contribution in just five years
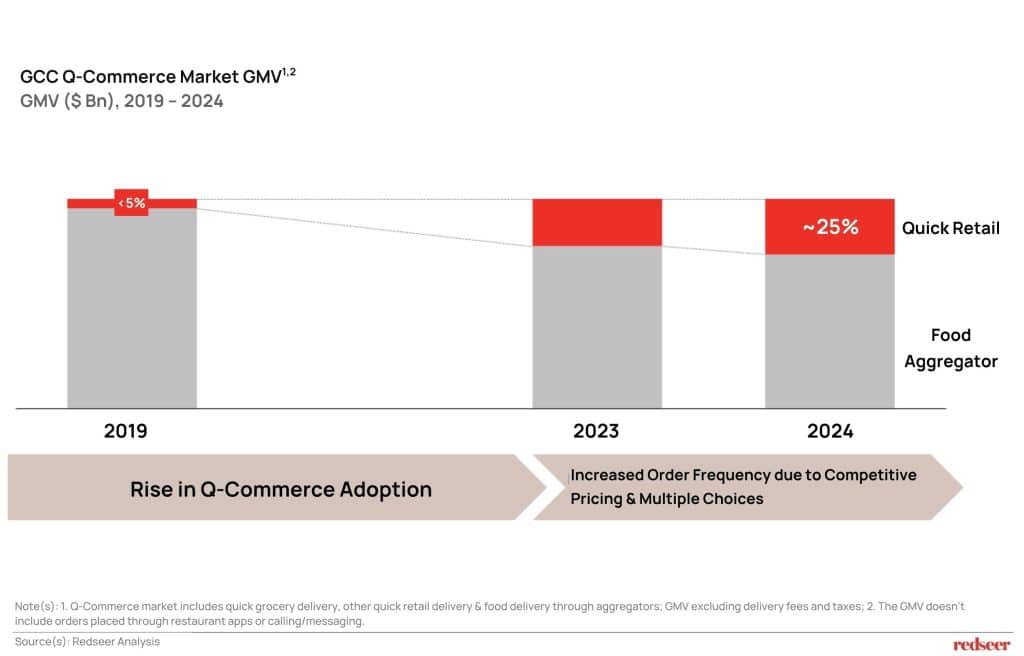
Quick Retail has surged from representing less than 5% of GCC Q-commerce GMV in 2019 to capturing ~25% by 2024—a five-fold increase in market share. This dramatic shift reflects both rising overall adoption and increased consumer spend across multiple categories. The growth has been fueled by competitive pricing strategies, subscription programs, and expanded choice offerings, with consumers increasingly viewing these platforms as comprehensive retail solutions rather than food-only services. This trend signals a fundamental change in consumer expectations and platform positioning.
Leading players like Hungerstation and Jahez saw a slight dip in GMV share despite achieving record-high figures, as their growth lagged behind the overall market. Their user base remained largely intact, indicating potential for a rebound. In contrast, smaller platforms such as ToYou, Mrsool, Mr. Mandoob, and Shgardi experienced sharp declines.
3. While several players have entered the segment with diverse value propositions…
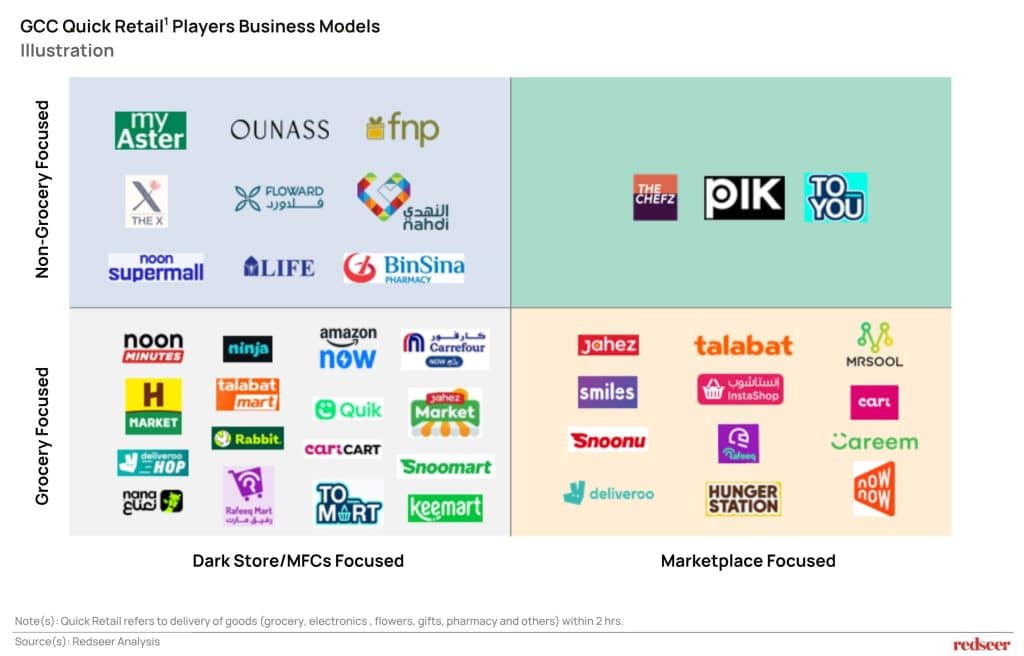
The Quick Retail space has attracted a heterogeneous mix of players pursuing varied strategic approaches. The competitive landscape spans grocery-focused operators like Talabat and Ninja, alongside non-grocery specialists such as Ounass and Floward. Business models range from dark store/Micro fulfillment centers-focused approaches (Amazon Now, Noon minutes, Hungerstation mart) to marketplace-driven strategies (Talabat, Jahez, Instashop). Some players such as TheChefz, PiK and ToYou focus on specialized categories through marketplace model, while others pursue broad category expansion. This diversity in value propositions and operational models reflects the multiple pathways to success within the rapidly expanding Quick Retail segment.
4. …market leadership specifically in both the UAE and KSA has continued to be volatile
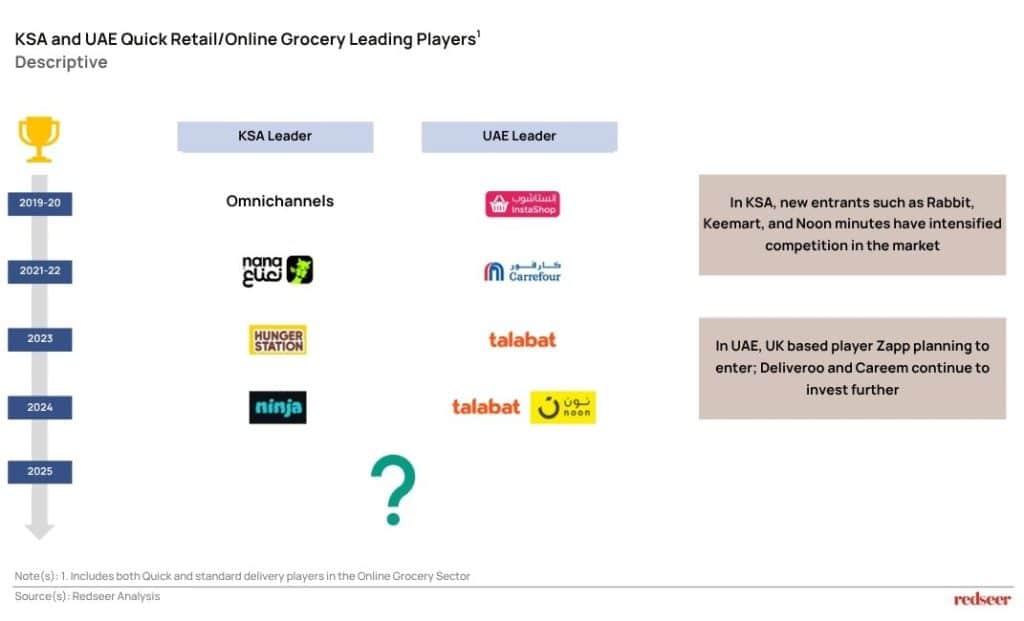
Despite strong sector growth, market leadership across key GCC countries remains fluid. In Saudi Arabia, the top spot has changed hands multiple times—from Omnichannels to Nana, then HungerStation, and most recently, Ninja. With new players entering the fray, it’s unclear who will lead in 2025. The UAE tells a similar story. After early dominance by Instashop, the lead passed to Carrefour, then Talabat, and now appears to be shared between Talabat and Noon. The competitive landscape is being reshaped constantly, with new entrants such as Rabbit, Keemart, and Noon Minutes turning up the heat in KSA, while Zapp’s anticipated entry into the UAE—alongside sustained investments from Deliveroo and Careem—signals more shifts ahead. This churn highlights just how dynamic and unsettled the race for leadership continues to be.
The GCC Quick Retail sector represents one of the most dynamic segments within the broader Q-commerce ecosystem, demonstrating exceptional growth while maintaining competitive fluidity. As platforms continue to expand their service offerings and new entrants challenge established players, the market is poised for continued evolution. Success will ultimately depend on platforms’ ability to build sustainable competitive advantages through superior execution, customer experience, and operational efficiency, rather than relying solely on promotional strategies. The next phase of this market’s development will likely determine which players can translate early market share gains into lasting leadership positions.