
Driven by Digitalization: Philippines Fintech
Philippines has a vast “underserved” banking population of ~57 million demonstrating the untapped potential in the country. Philippines lacks national ID system and hence the prevalence of financial frauds is also quite high. The new age fintech players with their latest technology and credit tools can tackle this issue well and thereby gain customer confidence leading to rising adoption of fintech solutions. The regulator is also creating a conducive FinTech ecosystem allowing players to grow their customer base and offer innovative solutions which the traditional players were not able to provide till now.
Here’s a deeper discussion on the Fintech landscape in the Philippines.
1. Digitalization has been a significant tailwind for the booming Fintech sector in the country.
We solve the strategy behind scale!
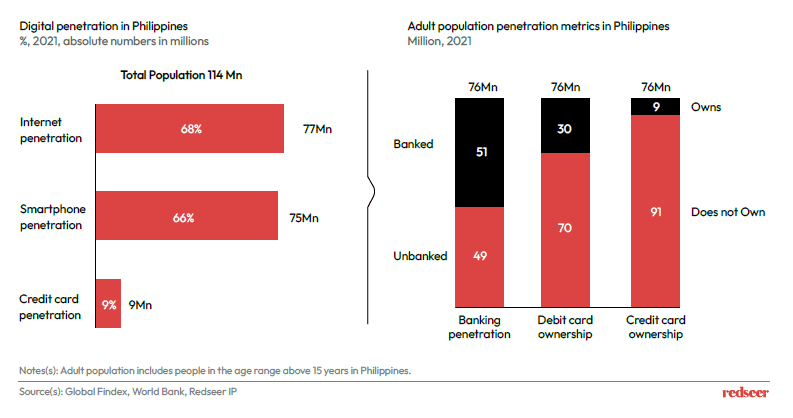
Philippines possesses an unbanked population of ~50% presenting huge untapped potential for Fintech players with rapid growth prospects.
The Fintech market is also driven by government’s push for financial inclusion and the consumer demand for cashless transactions. The regulators have been successful in providing a conducive environment for FinTech startups to flourish. With increasing internet and smart phone penetration rates, the adoption of FinTech solutions should rise in the country.
2. With an innovative and conducive regulatory framework, banking penetration is expected to rise rapidly in the country as users adopt new age fintech solutions
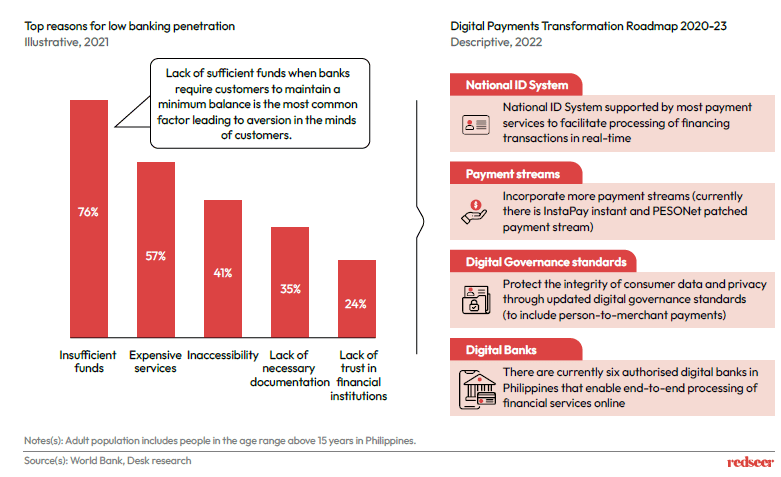
The adult “underserved” population of Philippines with no account state insufficient funds as the main reason for being unbanked/non-banked.
The country with its favourable regulatory policies and pro-digitalization agenda aims to convert 50% of its payments to digital by 2023. It has reinforced a digital payments transformation roadmap to achieve its target some of whose clauses are stated below.
3. While the industry’s top players’ offerings include e-wallet and digital payments, alternative lending and digital banks start-ups are on the rise
Vietnam has one of the highest growth rates for the eB2B sector compared to Indonesia and Philippines as it is still in a nascent stage and benefits from the small base effect. Unlike Philippines and Indonesia (archipelagos), Vietnam does not have geography related challenges.
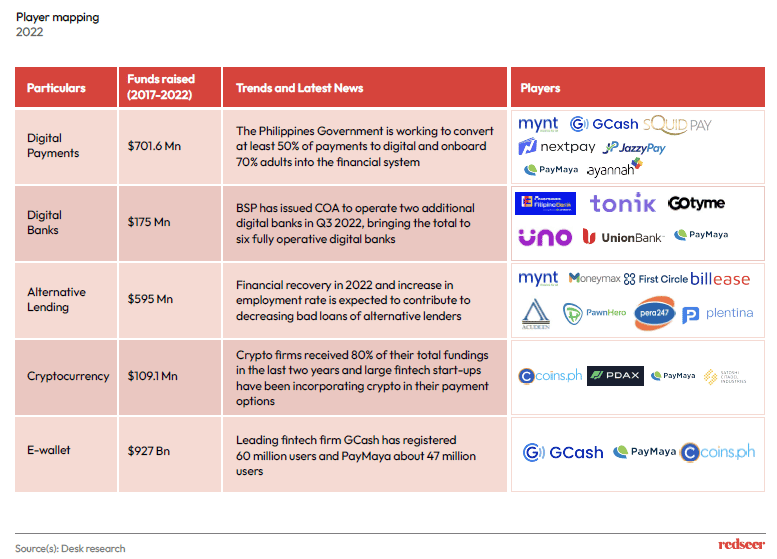
Majority of the investments in the sector have happened in e-wallets and digital payments segments and have now subsequently expanded to others. Embedded Finance is the newest disruption in fintech sector that is gaining traction. Web3, Insurtech, and wealthtech in Fintech are sectors to be on the lookout for in the coming years. We are focusing on alternative lending and digital banking in this NL.
4. The number of e-money accounts have proliferated in 2021 and surpassed the number of bank accounts signifying the huge prospects for Digital Banks
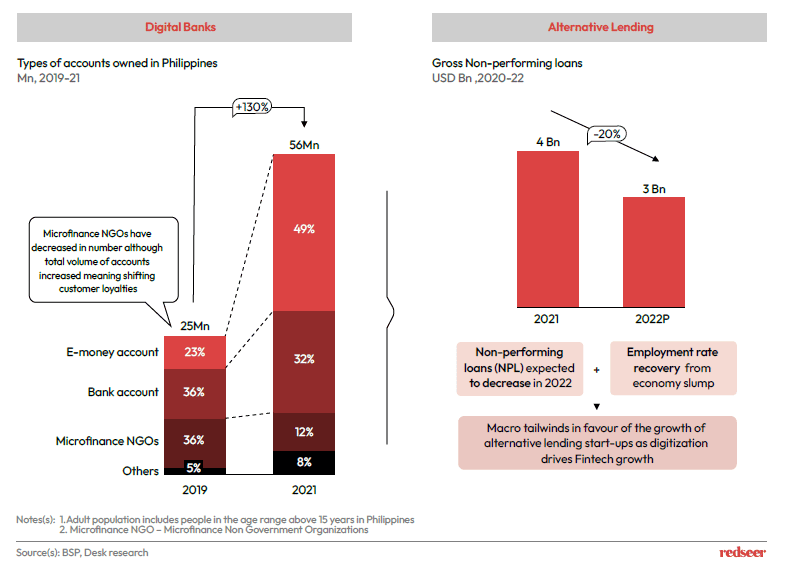
The number of e-money accounts overtook the number of bank accounts in 2021.
In terms of financial inclusivity, microfinance NGOs that once held a dominant position along with
bank accounts in 2019 have shown decline in numbers indicating shift in favour of e-money
accounts. Almost ~36% of the total adult population now possess an e-money account. The number
of e-money accounts have risen by 5x over 2 years boosting prospects for Digital Banks.
The general state of economy in the country is also improving and NPLs are expected to contract in 2022. These macro tailwinds are supportive for the growth of alternative lending posing lesser
risks from reduced NPL coverage from their capital.
5. SEA Fintech start-ups are experiencing significant flow of funds and the same is being observed in Philippines as well
Across India and Indonesia, tech enabled B2B players are offering wider stack of services. We can expect similar trajectory to be followed by players in Vietnam and Philippines wherein there is a two-pronged growth strategy that will be adopted by the players -widening stack of services to diversify the revenue base and penetrating outside tier 1 cities
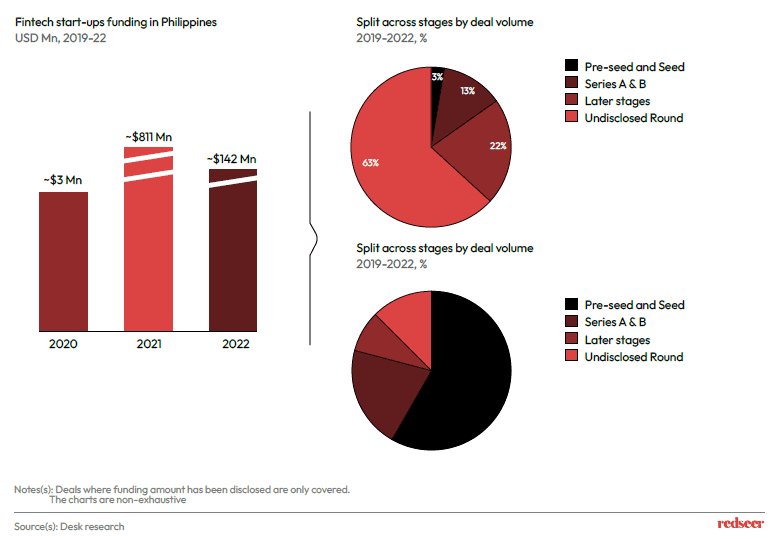
Payments and microlending are some of the sub sectors in the broader FinTech space that have attracted funding in Philippines.
Pre-seed and Seed fundings were the largest in terms of deal volume in the past three years signifying a lot of activity in the sector as new start-ups emerge.

Written by
Roshan Behera
Partner
Roshan is a Partner based in Singapore and focuses on Southeast Asia. His sector coverage includes e-commerce, logistics, fintech, eB2B, on-demand services, and other emerging sectors.
Talk to me
India’s Defence DeepTech Flywheel: The $6Bn Market Nobody’s Watching

Ready-to-Eat Brands Are Leaving 85% of Addressable Consumers on the Table

Who’s Winning in India’s Dating & Matrimony Market—and where are the opportunities for Platforms and Investors
